Introduction
Thailand joined the Global Methane Initiative (GMI) in 2008.
Thailand has a broad set of national climate action frameworks to support the country’s greenhouse gas reduction goals and reduce methane emissions. These measures include support for biogas as a renewable energy source, expansion of methane capture technologies in the waste sector, and use of new technology to reduce methane emissions in the agriculture sector. Thailand also participates in international collaborations to achieve global climate goals.
- Introduction
- Methane Emissions Summary
- Methane Commitments and Plans
- Methane Actions
- Ministries and Agencies Supporting Methane Actions
- GMI Delegates
Last Updated: October 2024
Methane Emissions Summary
Thailand has not published methane emissions data.
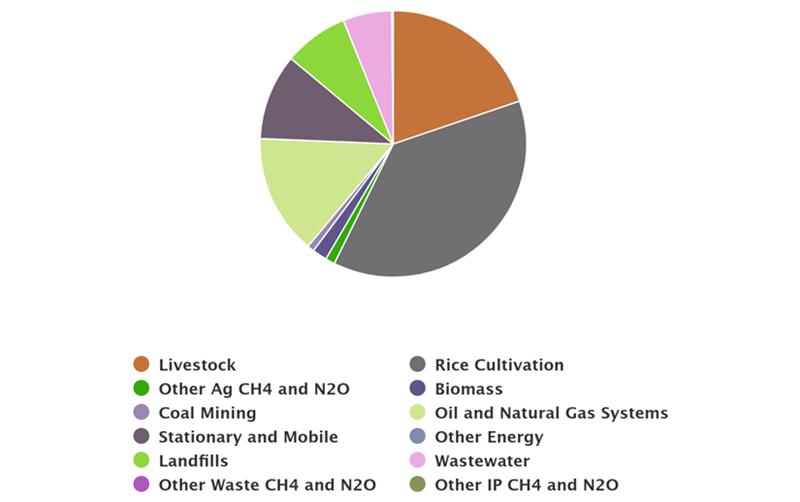
According to EPA’s non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Data Tool, Global Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emission Projections & Mitigation Potential: 2015-2050, the livestock sector accounts for approximately 20% of Thailand’s estimated methane emissions and oil & gas systems makes up about 15%. Rice cultivation accounts for more than 37% of methane emissions. The following charts illustrate the percentage of methane emissions by source for 2030 and provide estimates for projected methane emissions in Thailand through 2050. Data are presented in million metric tonnes carbon dioxide equivalent (MMTCO2e).
Methane Emissions by Source (Total = 96 MMTCO2e), 2030
Methane Emissions Trend and Projections by Sector, 1990-2050
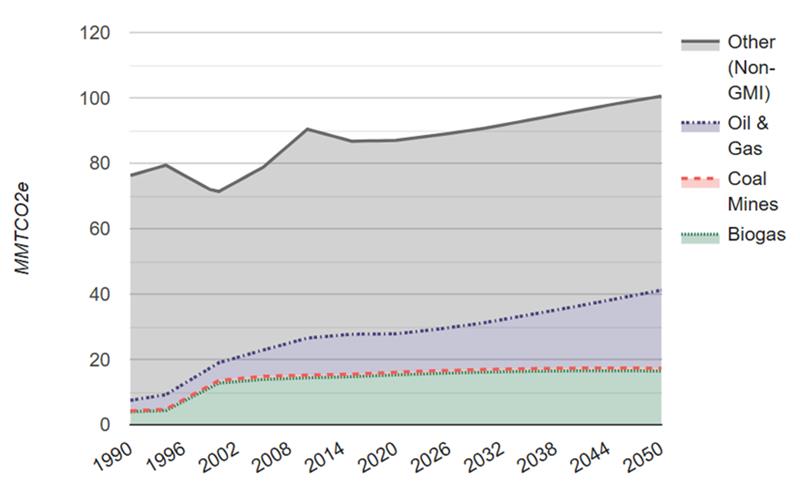
| Sector | 2020 | 2030 | 2050 |
| Biogas | 15.297 | 16.134 | 16.485 |
| Coal Mines | 0.797 | 0.804 | 0.841 |
| Oil & Gas | 11.742 | 14.287 | 23.871 |
| Other (Non-GMI) | 59.142 | 59.463 | 59.323 |
Source: Global Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emission Projections & Mitigation Potential: 2015-2050, U.S. EPA.
Methane Commitments and Plans
Methane mitigation efforts in Thailand are guided by national and international commitments and plans.
National
- Thailand’s Updated Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) commits to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, including methane, by 30% by 2030. The NDC also establishes the long-term goals of reaching carbon neutrality by 2050, and net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2065.
- Thailand published its Fourth Biennial Update Report on climate change in December 2022. The report summarizes greenhouse gas emission trends in Thailand, and reports on methane emission reduction activities including methane recovery and utilization at industrial wastewater management sites, and methane abatement in the agriculture sector.
- Thailand’s Mid-century, Long-term Low Greenhouse Gas Emission Development Strategy, published in October 2021, features measures to increase the utilization of methane at wastewater treatment sites, reduce methane emissions through enteric fermentation and manure management, and increase the production of biogas.
International
- Thailand has been a partner of the Climate and Clean Air Coalition since 2019, supporting activities to reduce methane and other short-lived climate pollutants.
Methane Actions
The following highlights a sampling of actions taken by Thailand to address methane, organized by GMI sector.
Biogas Sector
- Thailand’s 10-year Alternative Energy Plan (2012-2021) promotes the use of alternative clean energy and supports the expansion of biomass and biogas in the transportation sector.
Ministries and Agencies Supporting Methane Actions
Explore the following websites to learn more about the government ministries addressing methane emissions.

 Thailand
Thailand