Methane Mitigation: Lessons Learned from India’s Compressed Biogas Projects
India's CBG projects: methane mitigation through biogas conversion.
GMI Financial Readiness Framework for Organic Waste Management
This resource helps governments and developers secure financing, mitigate risks, and improve the viability of organic waste projects.
Waste Characterization Handbook:
Understanding Municipal Waste Streams to Develop Data-Driven Methane Mitigation Strategies
GMI Policymaker Framework for Addressing Methane Emissions
A step-by-step process and resources for policy development
How India’s Cleanest City Reduces Methane Emissions from Municipal Solid Waste
Case Study
Measurement, Reporting and Verification (MRV) Resource Center
A resource center providing information and tools to support the MRV of methane emissions and emissions reductions.
Biogas Sector
The GMI Biogas Subcommittee focuses on building capacity within Partner Countries to leverage common interests across the areas of agriculture, municipal solid waste, and municipal wastewater. These interests include biogas energy use, the types of wastes managed, waste treatment technologies, and the potential for synergistic projects involving input streams from multiple sources. Efforts include developing and promoting tools, policy guidance, and project development resources at the national, state, and city level within Partner Countries.
GMI Technical Groups
Within the Biogas Sector, GMI maintains active technical groups in the areas of agriculture, municipal solid waste (MSW), and municipal wastewater. These groups provide international leadership to mitigate global methane emissions through the abatement, recovery, and use of methane. They promote collaboration between delegates from Partner Countries and Project Network members to build capacity, develop strategies, and expand opportunities for using methane as a renewable energy resource.

Agriculture
Methane emissions come from livestock enteric fermentation, livestock waste management, rice cultivation, and agricultural waste burning.

Municipal Solid Waste
Municipal solid waste management and treatment activities such as landfilling and anaerobic digestion are sources of methane emissions worldwide.

Municipal Wastewater
Methane is produced when the organic material in municipal wastewater decomposes anaerobically.
Featured Resources
For a complete list of available biogas resources, including technical documents, presentations, and tools, please visit the resources page.

Solid Waste Emissions Estimation Tool (SWEET)
The Solid Waste Emissions Estimation Tool (SWEET) is an Excel-based tool that quantifies emissions of methane, black carbon, and other pollutants from sources in the municipal solid waste sector. The tool provides emissions and emissions reduction estimates at the project-, source-, and municipality-level. Cities can use this information for multiple purposes, including establishing a baseline scenario, comparing a baseline scenario to as many as four alternative scenarios, analyzing specific projects for potential emissions reductions, estimating the contribution of activities in the waste sector to overall city emissions reduction goals, and tracking progress over time, among other things

Anaerobic Digestion Screening Tool
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, on behalf of the Global Methane Initiative (GMI), developed the Anaerobic Digestion (AD) Screening Tool to assist stakeholders in assessing the potential feasibility of an AD project.

Landfill Gas Screening Tool (LFG-ST)
The Landfill Gas Screening Tool’s goal is to assist cities in assessing the potential feasibility of a landfill gas energy (LFGE) project. It provides a preliminary estimate of how much landfill gas (LFG) a site could collect, and whether that fuel supply is likely sufficient to support a modest-sized LFGE project. LFGE project types include combusting LFG directly to produce heat (e.g., for industrial applications), using LFG to generate electricity, and - in some cases - converting LFG into a compressed natural gas (CNG) to fuel vehicles.

OrganEcs Version 3.1
OrganEcs is a tool for estimating the costs associated with an organic waste management project. It provides planning-level assistance to local governments, waste professionals, policymakers, facility operators, and project developers to help them make financial decisions about their potential organic waste management projects.

Waste Characterization Handbook: Understanding Municipal Waste Streams to Develop Data-Driven Methane Mitigation Strategies
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency on behalf of the Global Methane Initiative developed the Waste Characterization Handbook and accompanying Excel tool to help decision-makers and solid waste professionals plan and conduct waste characterization studies to understand the composition of waste streams. Waste characterization data can be used to inform improved waste management planning and implementation and measure methane mitigation from these strategies.

Biogas Wastewater Assessment Technology Tool (BioWATT)
The Biogas Wastewater Assessment Technology Tool (BioWATT) provides a quick and preliminary assessment of wastewater-to-energy projects. Through BioWATT, users can receive a specific summary of their biogas production estimates for various wastewater-to-energy technologies, electricity generation potential from the produced biogas, greenhouse gas savings associated with biogas-generated electricity, and more.

Methane Mitigation from Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants
This fact sheet provides an overview of methane emissions generated in both wastewater collection systems and at wastewater treatment plants (WWTP). Topics include wastewater collection systems, conventional activated sludge (CAS) treatment systems, aerobic/aerated lagoon treatment systems, and anaerobic lagoon treatment systems. Biosolids management and opportunities for methane mitigation and use are also described.

Training Series: Best Practices for Landfill and Organic Waste Management
In 2024, the U.S. EPA, in collaboration with the Asian Development Bank and in support of the aims of the Global Methane Initiative (GMI) Biogas Subcommittee, hosted a four-part training series: Best Practices on Landfill and Organic Waste Management. The training focused on proven approaches and case studies for dumpsite closure and remediation; sanitary landfill construction, operation, and maintenance; organic waste treatment; feedstock management; greenhouse gas (GHG) measurement, reporting, and verification; and useful tools and resources. The training was initially delivered to implementers of the Bahawalpur Integrated Solid Waste Management project in Pakistan, but the training materials are broadly applicable to national and subnational decision-makers and policymakers, waste professionals, waste facility operators, and project developers.

Global Methane Initiative (GMI) Policymaker Framework for Addressing Methane Emissions
The Global Methane Initiative (GMI) Policymaker Framework for Addressing Methane Emissions (the Framework), is designed to help energy and environmental policymakers address methane emissions systematically to accelerate progress toward national or subnational methane emissions reduction goals. The Framework depicts a step-by-step process for developing and implementing policies and programs to measure and reduce methane emissions economy-wide or in specific methane-emitting sectors, such as oil and gas, coal, and biogas. It provides links to helpful resources from GMI and other organizations that can help policymakers implement each step.

Methane Mitigation: Lessons Learned from India’s Compressed Biogas Projects
The U.S. EPA, in collaboration with The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) of India, released an analysis entitled, “Methane Mitigation: Lessons Learned from India’s Compressed Biogas Projects.” This report assesses facilities that mitigate methane emissions by generating compressed natural gas (CNG) from biogas feedstocks, such as livestock manure and agriculture waste, utilizing anaerobic digesters, in India. The report summarizes the developmental and operational challenges for such “Compressed BioGas (CBG)” plants, specifically focusing on the challenges and opportunities that stakeholders face in the development and operation of CBG plants. Recovering methane from agriculture and food waste and converting it to energy resources is critical to methane mitigation efforts in India and energy security in developing countries.

Establishing Biogas-Powered Cold Storage in Rural India for Methane Mitigation and Sustainable Food Systems
Mitigating post-harvest food loss can result in economic benefits for farmers, increase food security, and reduce methane emissions from organic waste. Each year, an estimated 30 percent of fruits and vegetables produced in India are lost or wasted despite the country ranking 94th out of 100 on the 2020 Global Hunger Index (HLPE, 2014; Agarwal et al., 2021). Almost half of post-harvest food losses in India are attributed to the lack of a reliable cold chain, the integrated network of refrigerated storage facilities, transportation, and merchandising technologies that maintain food quality moving from harvest to the consumer (Peters et al., 2019). Cold-chain technologies are energy intensive and typically powered by fossil fuels. In recent years, there has been a focus on clean energy powered cold-chain solutions, including renewable energy powered cold storage facilities that store commodities after harvest.

How India’s Cleanest City Reduces Methane Emissions from Municipal Solid Waste
A case study on Indore’s waste management keys to success: Indore, the largest city in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India, has consistently ranked the “cleanest city in India” since 2017. In October 2023, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, on behalf of the Global Methane Initiative, conducted a study tour of Indore that brought other waste management officials to learn about Indore’s improved waste management. This case study provides an overview of the factors that contributed to the successful transformation of Indore’s waste management system, including leadership buy-in, public engagement and participation, pilot testing, infrastructure upgrades, and innovative financing. It can serve as a model for cities around the world to improve solid waste management and reduce methane emissions and other climate pollutants.

Biogas Subcommittee
Subcommittee Co-chairs
Godfred Fiifi Boadi, Chair
Ministry of Sanitation and Water Resources
Ghana
Subcommittee Members
Representatives from 29 countries participate in the Biogas Subcommittee.
Project Network
Hundreds of Project Network members support methane abatement projects in the biogas sector.
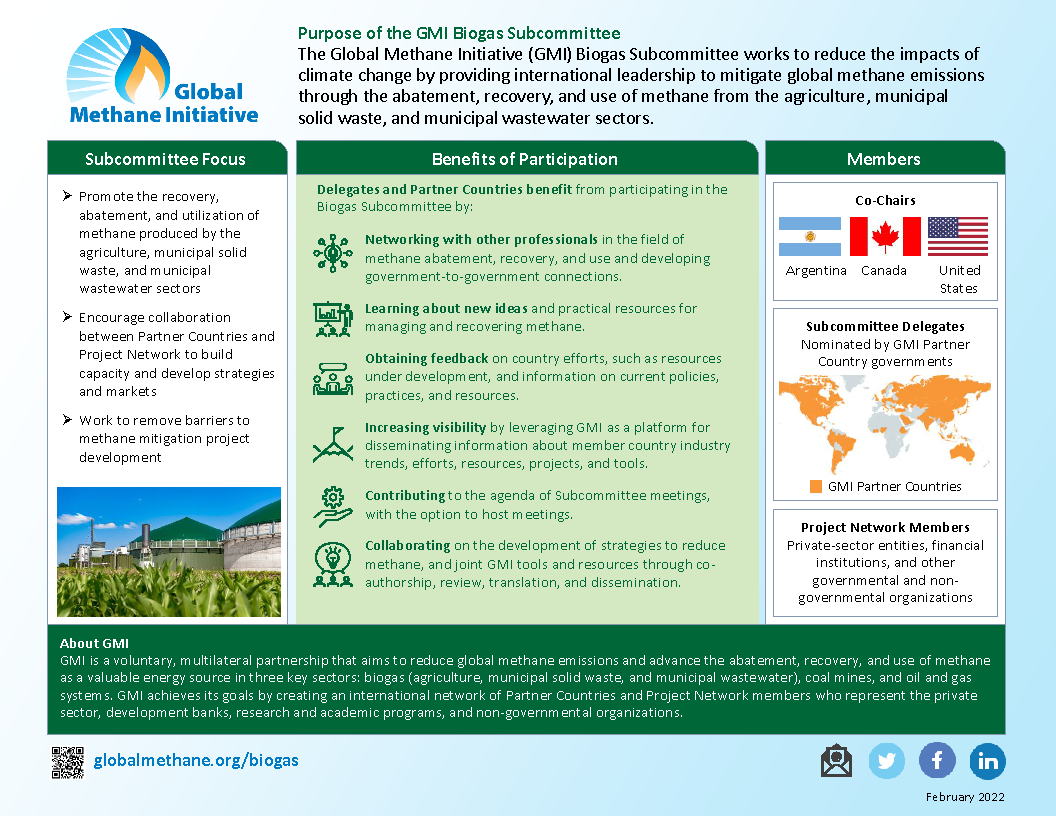
Biogas Subcommittee Statement of Purpose
Global Methane Initiative (GMI)
Leading methane action since 2004